In today’s digital age, both EHR and EMR are transforming how patient information is stored, shared, and utilized. Though these terms are often used interchangeably, Electronic Health Records (EHR) and Electronic Medical Records (EMR) serve distinct purposes in healthcare, especially for US providers who must comply with stringent regulations. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions about healthcare management, improving patient care, and optimizing practice operations. This guide breaks down the key features, benefits, and drawbacks of EHRs and EMRs, offering clarity on how they impact healthcare practices in the US.
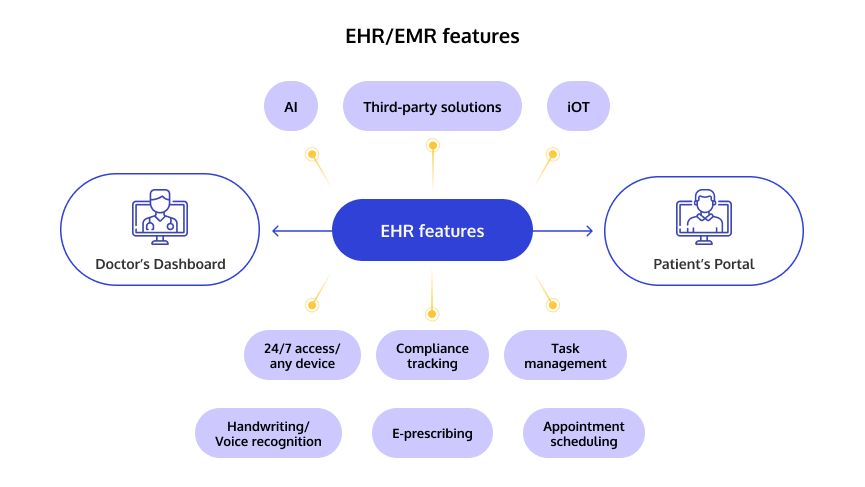
Everything You Need to Know About Electronic Health Records – EHR
What Does EHR Stand For?
An Electronic Health Record (EHR) is a digital record of a patient’s comprehensive health information, stored in a format that is accessible to authorized healthcare providers across different settings. EHRs go beyond a single provider’s medical office, enabling seamless information sharing across healthcare organizations and allowing providers to offer a well-rounded, patient-centered approach.
Pros and Cons of EHR
| Pros | Cons |
| Accessible across multiple healthcare settings | Initial costs can be high |
| Promotes coordinated, patient-centered care | Requires time and resources for training |
| Enhances patient safety with real-time data | Risk of data breaches without strong security |
| Meets US compliance standards (e.g., HIPAA) | Some systems may experience technical issues |
Is EHR Ideal for US Providers?
EHRs are widely recognized as an ideal solution for US providers because they streamline data sharing, allowing healthcare professionals to quickly access a patient’s full health history. This interoperability helps ensure compliance with HIPAA and Medicare/Medicaid requirements, promoting efficient, integrated care for patients nationwide.
Is it Easy to Use EHR?
EHR systems have improved significantly, becoming more user-friendly and efficient for providers. Most reputable EHR vendors offer extensive training to ensure smooth implementation, and many EHR systems now have intuitive interfaces. However, usability can vary by vendor, so it’s important for providers to choose an EHR system that aligns with their specific needs and workflows.
Everything You Need to Know About Electronic Medical Records
What Does EMR Stand For?
An Electronic Medical Record (EMR) is a digital version of a patient’s paper chart, storing information such as medical history, diagnosis, medications, and allergies within a single practice. Unlike EHRs, EMRs are generally limited to one provider’s office and are not designed to be shared across different healthcare settings.
Pros and Cons of EMR
| Pros | Cons |
| Digital version of paper records for easy access | Limited interoperability |
| Reduces paperwork and physical storage needs | Requires additional steps to share externally |
| Ideal for diagnosis and treatment within one practice | May lack comprehensive patient view |
| Lower upfront cost than EHR | Limited functionality for patient-centered care |
Is EMR Ideal for US Providers?
EMRs can be suitable for smaller practices focused on specific aspects of patient care and may work well in settings where data sharing with other providers is not essential. However, larger healthcare organizations or those seeking comprehensive patient management and regulatory compliance often benefit more from EHR systems.
Is it Easy to Use EMR?
EMRs are generally easier to implement and use for smaller practices. With fewer complex features than EHRs, they typically require less training, though providers should be prepared for updates to comply with healthcare regulations. However, the inability to easily share data with other providers can hinder coordinated care, impacting patient outcomes.
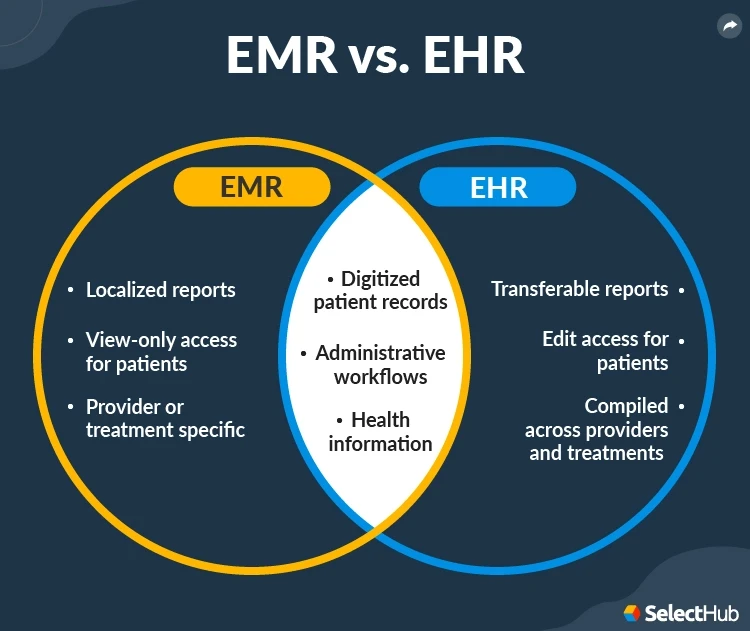
What Are The Differences Between EHR and EMR?
1. Accessibility Across Multiple Healthcare Settings
- EHR: Designed for use across different healthcare organizations, allowing seamless information sharing for coordinated care.
- EMR: Limited to a single healthcare provider’s office and not designed for external sharing.
2. Level of Patient Information Available Between EHR and EMR
- EHR: Provides comprehensive health information beyond the basic medical history, including lab results, demographics, and lifestyle data.
- EMR: Primarily includes medical history and treatment notes pertinent to a single provider.
3. Interoperability and Data Sharing by EHR and EMR
- EHR: Facilitates data sharing across providers, specialists, and even with patients for integrated care.
- EMR: Not intended for interoperability; information sharing may require manual transfer or printing records.
4. Support for Patient-Centered Care With EHR and EMR
- EHR: Enhances patient engagement by allowing patients to access and contribute to their health records.
- EMR: Focused more on clinician needs for diagnosis and treatment within the practice, with limited patient involvement.
5. Compliance and Regulations for EHR and EMR
- EHR: Meets US regulatory standards like HIPAA and MIPS for security, interoperability, and “meaningful use.”
- EMR: May meet HIPAA standards but generally lacks compliance features required for Medicare/Medicaid incentives.
6. Usability for Decision-Making on EHR and EMR
- EHR: Provides tools for data analytics, decision support, and evidence-based practice, helping providers make well-informed decisions.
- EMR: Offers limited decision-support tools, mainly used for recording patient information within the office.
7. Information Portability with the Patient
- EHR: Information moves with the patient to different providers, enhancing continuity of care.
- EMR: Information does not automatically transfer with the patient and may require manual sharing.
8. Real-Time Access to Data With EHR and EMR
- EHR: Enables real-time access to patient information, essential for urgent care and emergency responses.
- EMR: Information is accessible in real-time within the practice but lacks immediate sharing capabilities.
9. Cost and Implementation Complexity Difference Between EHR and EMR
- EHR: Higher upfront costs, but many systems provide a wide range of features and compliance support for larger practices.
- EMR: Lower cost and easier to implement, making it more accessible to smaller practices.
10. Patient Access to Records Using EHR and EMR
- EHR: Patients often have online access to their health data, promoting engagement in their own healthcare.
- EMR: Patient access is typically limited, and records may need to be printed or manually shared with patients.
| Feature | EHR | EMR |
| Accessibility | Across multiple organizations | Limited to one provider |
| Level of Detail | Comprehensive health information | Basic medical information |
| Interoperability | High, designed for data sharing | Low, mainly within the practice |
| Compliance Support | Meets HIPAA, MIPS, and Meaningful Use | Limited regulatory support |
| Cost | Higher, more complex implementation | Lower, simple implementation |
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between EHRs and EMRs is essential for providers and medical billing professionals in the US. While EMRs are useful for in-practice documentation, EHRs provide a broader, patient-centered solution for collaborative healthcare environments. EHRs excel in interoperability, patient engagement, and regulatory compliance, meeting the needs of modern healthcare more effectively than traditional EMRs. For providers focused on improving patient outcomes and navigating regulatory requirements, EHRs are a forward-looking investment in delivering quality, efficient care. Selecting the right system depends on each practice’s needs, patient volume, and budget—but for those aiming to optimize patient care and data accessibility, EHRs are often the preferred choice.
If you’re struggling with EHR and EMR records management and looking for a competent billing agency to take the pressure off your shoulders, QZ Medx is your go-to destination. Contact us today to shape the great healthcare records future.